Amid the Fourth Industrial Revolution, driven by groundbreaking advancements in Artificial Intelligence, 5G, and Internet technologies, we are witnessing the rise of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and digital transformation in the manufacturing market.
Implementing these technologies in manufacturing can:
- Reduce OPEX by up to 27%
- Achieve next-generation monitoring and control mechanisms
- Be on par with the competition:
This article is a detailed overview of the IoT in idustrial setting and the ways to adopt it in your organization.
What drives IoT in Manufacturing?
IoT smart manufacturing is reshaping the industry landscape, and the numbers speak volumes: the Internet-of-Things application in the manufacturing industry is set to skyrocket from USD 0.39 trillion in 2024 to an astounding USD 1.22 trillion by 2029. Furthermore, the global predictive maintenance market witnessed an 11% growth in 2022, and it’s projected to continue with a CAGR of 17% until 2028. These figures underscore the undeniable influence of IoT in manufacturing.
By the end of 2020, manufacturing accounted for 34% of all industrial IoT applications. Over 80% of manufacturing companies recognize IoT as essential for their future success. And it’s not just the industry giants; small manufacturers that used IoT have experienced a 10% revenue boost. Clearly, IoT’s impact is pervasive and transformative.
So, what exactly is IoT? What does this mean for your manufacturing business, and how can you implement it? This comprehensive guide will explore the benefits, potential pitfalls, future trends, and actionable steps for building smarter manufacturing with the Internet of Things. And the best part? You can achieve all of this without spending millions of dollars. Stay tuned to unlock the power of IoT and revolutionize your manufacturing operations.
What Does IoT Stand for in Manufacturing?
The Internet of Things (IoT) in manufacturing – is a network of connected devices and machines which are seamlessly integrated into machinery, equipment, and various production processes that collect, exchange, and analyze real-time data. This network of industrial IoT products empowers manufacturing by offering real-time insights for improved decision-making and helps to track and control equipment performance, product quality, and environmental conditions throughout the entire production process, paying attention to the smallest detail for future performance enhancements.
What is the convergence of OT and IT?
The convergence of IT and OT is crucial in unlocking the full potential of IoT in manufacturing. Operational Technology (OT) involves all the hardware, such as sensors and software, used to monitor and control physical devices, such as machinery and equipment. On the other hand, Information Technology (IT) focuses on computing systems, data storage, and networking infrastructure, managing the flow of information within an organization.
In the context of IIoT, the convergence of OT and IT enables manufacturers to:
- Enhance Security: By fusing OT and IT security strategies, manufacturers can shield their assets from cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
- Optimized Operations: Real-time data from OT devices and advanced analytics from IT systems allow for better decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Improve Collaboration: Merging OT and IT teams fosters a collaborative environment, simplifying IoT implementation and troubleshooting.
- Improved Decision-Making: Access to real-time data insights from OT and IT systems empowers decision-makers to make decisions that drive business success.
- Increased Productivity: With OT and IT working in harmony, manufacturers can fine-tune resource allocation, reduce waste, and boost productivity across the board.
Without this convergence, the promise of IoT manufacturing remains unfulfilled, lacking the transformative impact on production.
While some manufacturers may be hesitant due to concerns about complexity, cost, or change resistance with IT/OT integration, the benefits are compelling:
- IT/OT integration enables real-time monitoring and control of production processes, improving operational efficiency, reducing downtime, and optimizing resource utilization.
- By combining IT and OT systems data, manufacturers gain valuable insights that empower better decision-making, driving innovation and competitiveness.
- Integrating IT and OT security strategies strengthens defenses against cyber threats, safeguarding sensitive manufacturing data and intellectual property.
- A unified IT/OT infrastructure provides a scalable and flexible platform that can adapt to changing business requirements and technological advancements.
- With increasing data privacy and security regulations, IT/OT integration helps manufacturers ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
While integrating IT and OT systems may present initial challenges, the long-term benefits far surpass any drawbacks. Manufacturers who embrace this integration are better equipped to navigate today’s complex manufacturing landscape, drive operational excellence, and seize growth and innovation opportunities.
You might also like
iot
How to Remote Access IoT Devices
In the last twenty years, the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape has grown immensely. This marks significant strides in how computers and devices help our daily tasks and complex applications. IoT consists of a vast network of sensors, devices, and systems. They’ve become crucial to our lives, letting us remotely connect with many devices. This […]

How to implement IT/OT in manufacturing?
So, we figured out all the buzz about IT/OT and IIoT in manufacturing. At Pragmatic DLT, we craft custom software and offer IT strategy consulting. We’re experts at making IT/OT solutions in manufacturing easier to use through a clear, step-by-step approach tailored just for you. Here’s how we can help you make the most of IoT in manufacturing:
We first conduct a Discovery Session (up to five days). Then, we host a series of group workshops with all stakeholders to understand your project’s objectives, goals, and limitations. Together, we sketch out an initial vision and solution architecture that aligns perfectly with your business needs, setting the stage for a successful rollout.
The second stage is the Proof of Concept (up to three months). It is about tackling your project’s trickiest and most uncertain parts. By coding the riskiest tech scenarios, we can help you figure out what to do about any uncertainties and ensure your project plan is doable. This proactive approach lets us spot, fix, and identify potential gaps or risks early on so you can move on to the development phase with less stress.
Once the previous stages are completed, PDLT will help you roll out the solution across your organization. This includes building a solid foundation for further development and scalability. It ensures that your IT/OT solution can adapt and scale to support your manufacturing needs.
How does IoT work in Manufacturing?
Industrial IoT can help organizations transform age-old factories into smart manufacturing. A combination of key technologies powers this transformation:
- Sensors and Actuators: These components, like flow sensors, pressure sensors, and temperature sensors, act as the eyes and ears of IoT manufacturing. They monitor various aspects such as machine performance, output, quality control, and environmental conditions. Actuators respond to this data, adjusting operations to optimize performance.
- Radiofrequency identification (RFID) tags and barcode scanners accurately track and identify items on assembly lines. They ensure quality control by identifying materials, parts, and products.
- Connectivity Technologies: Wired protocols (like Ethernet or Fieldbus) and wireless connections (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, LPWAN, LORA, Sigfox, and cellular networks) link devices and systems. These connections ensure seamless data flows to central hubs or cloud platforms, maintaining sync.
- Cloud computing: Cloud platforms provide storage, computing power, and analytics capabilities for vast amounts of IoT-generated data. Centralized monitoring and management allow manufacturers to derive actionable insights, improving decision-making and driving efficiency. Popular cloud IIoT platforms include Google Cloud IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, and Amazon Web Services IoT.
- Edge computing: Devices like gateways, industrial PCs, and embedded systems analyze data close to the source, reducing the need to send all data to the cloud. This approach facilitates faster decision-making, lowers latency, and optimizes network bandwidth usage.
- Data analytics tools: Advanced technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) extract insights from the collected data. These insights drive improvements in areas like predictive maintenance and quality optimization, enhancing process efficiency.
- Security technologies: Robust cybersecurity measures protect the interconnected network by encrypting devices, securing communication channels, and safeguarding sensitive data.
- Application development tools: Specialized tools are essential for building, managing, and integrating IoT applications. These platforms offer features like device management, data visualization, and application development tools. Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) enable seamless communication across devices, applications, and cloud services.
- Integrating IoT with existing systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), manufacturing execution systems (MES), and product lifecycle management (PLM) software enhances manufacturing operations. This comprehensive approach boosts efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
Together, these technologies enable manufacturers to harness IoT’s full potential, driving efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
10 IoT Use Cases in Manufacturing that You Can Implement Right Now / Examples of IoT technologies in Manufacturing
In this case, IoT provides millions of capabilities to revolutionize manufacturing processes and secure a strong competitive advantage. Below, we outline ten ways manufacturing businesses can harness the power of IoT technology to drive innovation and stay ahead in the market:
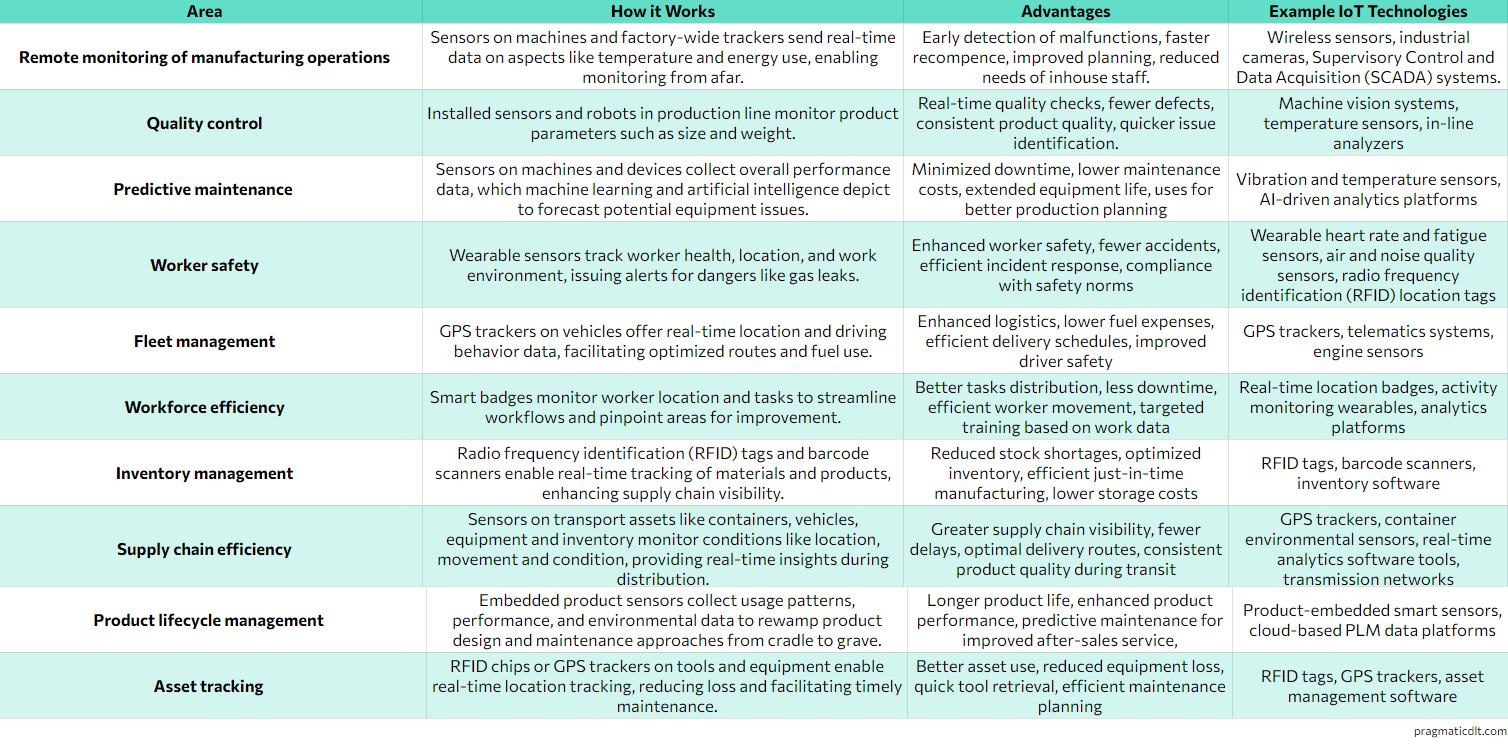
Remote monitoring of manufacturing operations
One of the standout benefits of the Internet of things in industry is monitoring production processes from anywhere. With connected devices and sensors, manufacturers can keep tabs on key performance indicators (KPIs) and fetch valuable insights in time, which provides flexibility and control, for quick decision-making, boosting efficiency and minimizing downtime.
Quality control
IoT technology empowers manufacturers to implement robust quality control measures across factories. By integrating sensors and automated inspection systems (statistical process control) or defect detection, which can detect and debug all malfunctions on every product stage, ensuring only high-quality products hit the shelves.
Predictive maintenance
IoT devices provide manufacturers with the ability to analyze data and effectively forecast machine outages before they escalate. This enables manufacturers to schedule timely maintenance in order to minimize downtime, slash costs, detect anomalies, predict different failures and extend the life cycle of their equipment.
Worker safety
The Internet of Things in manufacturing plays a pivotal role in fostering a secure work environment. Wearable sensors and devices can monitor environmental conditions, employee activities, and equipment operations to pinpoint potential workers safety and alert them of potential accidents.
Fleet management
In order to manage a fleet of vehicles or machinery, IoT offers advanced fleet management solutions for manufacturers. With real-time tracking of assets, automated maintenance scheduling, and route optimization, logistics can run smoothly and cut unnecessary costs.
Workforce efficiency
IoT helps boost productivity by offering real-time data about employee performance and productivity. Data-driven analytics can identify ways to improve, slick workflows, and optimize operations, leading to increased output and reduced labor costs.
Inventory management
IoT sensors keep an eye on stock levels, track assets in real-time, and send automated alerts for reordering, so you always have the right amount of inventory.
Supply chain efficiency
Supply chain management gets a lot easier with operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) convergence and IoT technologies. By connecting suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors through IoT enabled platforms, you can see what’s going on in your supply chain: by tracking the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products; which means you can make decisions faster about some improvements and run your business more efficiently.
Product lifecycle management
IoT manufacturing solutions for product lifecycle management is a great choice because it lets manufacturers collect real-time data on how their products are performing and being used. This data helps them make better products, keep customers happy, and come up with new ideas for future products.
Asset tracking
Industry IoT devices let you track your assets in real time, so you always know where they are, what they’re up to, and how they’re being used. This helps you make better decisions about how you use and protect your resources.
The integration of OT and IT through IoT implementation in manufacturing is revolutionizing the industry, driving efficiency, productivity, and innovation to new heights. Manufacturers that embrace this convergence will stay ahead of the overall market and pave the way for a more up to date and connected future of manufacturing.
Pros of integrating Internet of Things in industry:
- Monitoring entire production line from machine performance to tracking inventory lets you fine-tune workflows, boosting overall efficiency and cranking up your output quantity or quality;
- IoT devices handle repetitive jobs, slashing labor costs, while ramping up productivity, helping in labor-saving automation.
- Spotting defects in real-time means you catch quality issues before they escalate, ensuring your products meet the highest standards.
- By predicting equipment issues before they happen, you cut down on downtimes and keep things running smoothly.
- Keeping tabs on what your clients want and how they consume your products in real-time ensures you’re always ready to meet customer demands, enhancing their overall experience.
- Industry IoT devices provide real-time visibility into supply chain operations, enabling better decision-making.
- IoT enables manufacturers to adapt shiftly to changing market conditions and customer demands.
- Improved efficiency and predictive maintenance with reducing waste can lead to significant cost savings;
- Real-time data from IoT devices becomes your secret weapon. It guides smarter decisions across production planning, scheduling, and resource allocation.
Main challenges of IoT implementation:
- Data integration: Integrating IoT devices with existing systems can be challenging, requiring significant time and effort to ensure seamless communication between devices and platforms.
- Legacy Systems: many manufacturing facilities still rely on older machines and software that may not be compatible with IoT, making it difficult to connect them with modern IoT devices.
- Ensuring interoperability between different IoT devices from different manufacturers can be a challenge, sometimes requiring additional customization or middleware.
- There may be skill gaps within the manufacturing industry, as IoT is a relatively new field, requiring training and knowledge to effectively implement and manage IoT systems and not everyone has the skills needed to implement and manage these systems effectively.
- Shifting to IoT can unsettle employees used to old ways of doing things, requiring careful change management.
- Security concerns are also a significant challenge, as more devices connected to the internet means a higher risk of cyberattacks and breaches, necessitating complex and costly robust security measures.
- While IoT offers long-term benefits, the initial investment can be significant, covering new devices, software, training, and infrastructure upgrades.
- Ensuring the reliability and downtime of IoT devices in harsh manufacturing environments can be challenging, meaning any malfunction can disrupt operations, requiring a focus on device reliability and uptime.
In summary, while IoT offers exciting possibilities for improving efficiency and productivity in manufacturing, it’s not without its challenges. From integrating diverse data sources and navigating legacy systems to addressing skill gaps and managing change, manufacturers have their work cut out for them. However, with careful planning, investment in training, and a willingness to adapt, these challenges can be overcome, paving the way for a smarter, more connected future in manufacturing.
Conclusion
IoT can make manufacturing safer, more efficient, and more profitable. While there are certain challenges that you need to overcome in IoT devices implementation like data integration, legacy systems, and security concerns. It might cost more upfront and require more planning, but the path to a more efficient manufacturing future is both possible and worthwhile. With IoT in manufacturing you can: monitor production processes, implement robust quality control, predict maintenance needs, ensure worker safety, streamline inventory and supply chain management and adapt to changing market demands swiftly.
This approach is a superior advantage for those who want to stay ahead of the competition. Are you ready to take advantage of all that IoT has to bring to your manufacturing operations? Get in touch with our experts today.